This is the second blog in a series exploring natural alternatives to reduce stress and manage mild to moderate mental health problems such as anxiety, depression and ADHD symptoms. If you haven’t read part one in this series, then I suggest you start there first.
Lemon Balm (melissa officinalis)
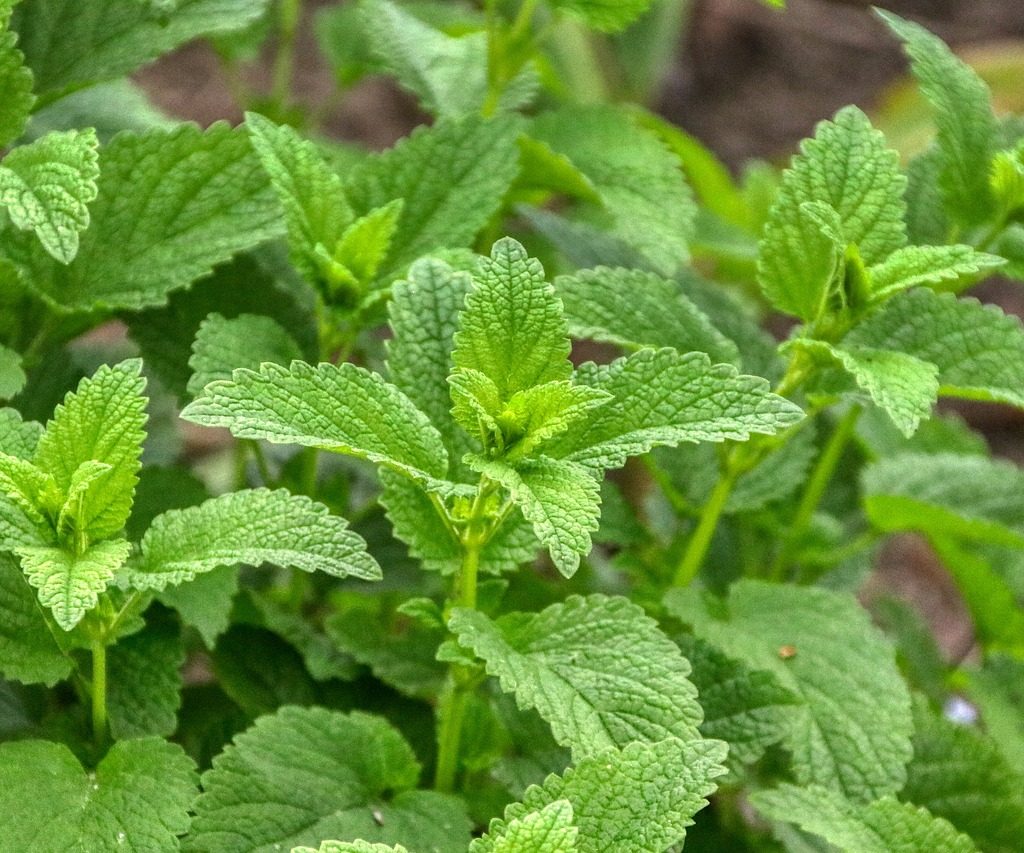

With its long history in Greek medicine, lemon balm was affectionately referred to as an elixir of life, for its reputation for prolonging one’s life. Greek physicians encouraged drinking lemon balm to make the heart merry, revive spirits and do away with melancholy. In 1696 the London Dispensary stated the balm steeped in wine would reverse aging and “relieve languishing”. The Arabs also talked about its calming and healing properties for steadying nerves and a remedy for heart palpitations. Perhaps they were onto something, as more recent studies in patients with chronic stable angina demonstrated decreases in depression, anxiety, stress, and sleep disorders after taking lemon balm supplements. There are also good, published results for women experiencing the post-partum blues after caesarean births. The oil in lemon balm has a sedative effect which reduces tension and stress. There are anecdotal reports of many a student benefiting from the herbal tea, just prior to sitting exams, to calm the butterflies, clear their head and sharpen the memory. Lemon balm tea is safe for all ages – even an unsettled baby to help with sleep.
Affectionately known as ‘melissa’ in some countries, lemon balm is a good companion plant in the garden. Some people plant it near their beehive to settle bees into their new home and prevent swarming. Lemon balm will grow in sun or shade, and it won’t take over like its mint cousin. Propagate it by cutting, root division or seed.
Make a tea with one heaped teaspoon of chopped, fresh leaves in a cup of boiling water, 2-3 times a day. It’s also a lovely refreshing drink, when chilled, or makes a nice addition to fresh fruit salad. It can also be added to the bath for a relaxing body soak.
Lemon balm should not be consumed if taking thyroid hormones.
Hops (humulus lupus)
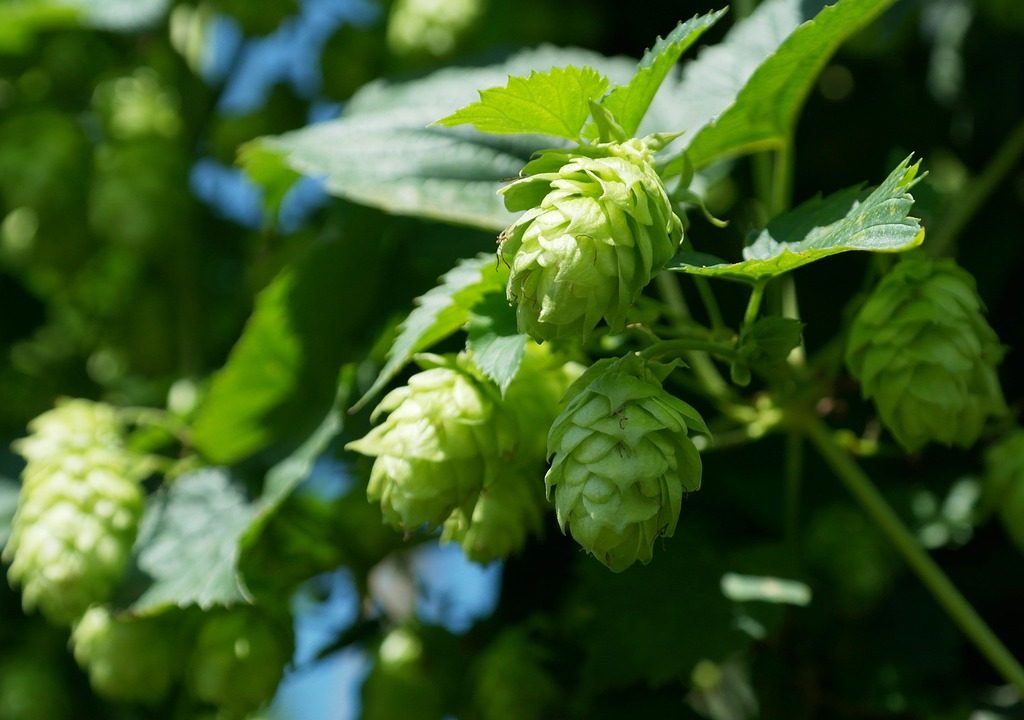

Hops is a member of the Cannabaceae (marijuana) family. Native Americans were some of the first to discover the sedative effects of hops, back in the 9th century. In 16th Century Europe, hops were widely used as a herbal tonic that offered calming, sedative, and sleep-promoting properties, not just as an ingredient to prevent beer spoiling. The Chinese started using hops to treat insomnia, restlessness and nervous tension in the 19th Century. In 2017, a study of healthy young adults experiencing mild anxiety and depression were treated with hop extract for one month, demonstrating significant reductions in symptoms. Whilst a few studies suggest hops has the ability to treat anxiety and mood disorders, more research is needed to confirm these effects. Anecdotally and historically, hops calm the central nervous system and relaxes muscles, soothing worries and tension.
The vine from hops will very quickly cover a pergola or trellis. It requires a rich soil and warm sunny position in the garden. In subtropical gardens, the plant appreciates afternoon shade. Propagation is by seed, cuttings or root divisions with buds. Female plants are preferable to produce an abundance of the strobiles, the cone-shaped fruit used in making the medicinal tonic, however male plants are needed if you wish to collect seed.
Dried or fresh hops can be used with vodka or another flavourless alcohol to make a tincture which will keep for many months. Hops can also be used to make a tea or stuff a pillow along with other more pleasant-smelling herbs, to put beside your head at night to aid sleep.
If you have a history of trauma its best to avoid hops to begin with and use an alternative nervine such as skullcap or blue vervain, until you are well into your healing journey. There are no known side effects or contraindications for using hops, however, always consult your doctor if introducing it to your treatment plan.
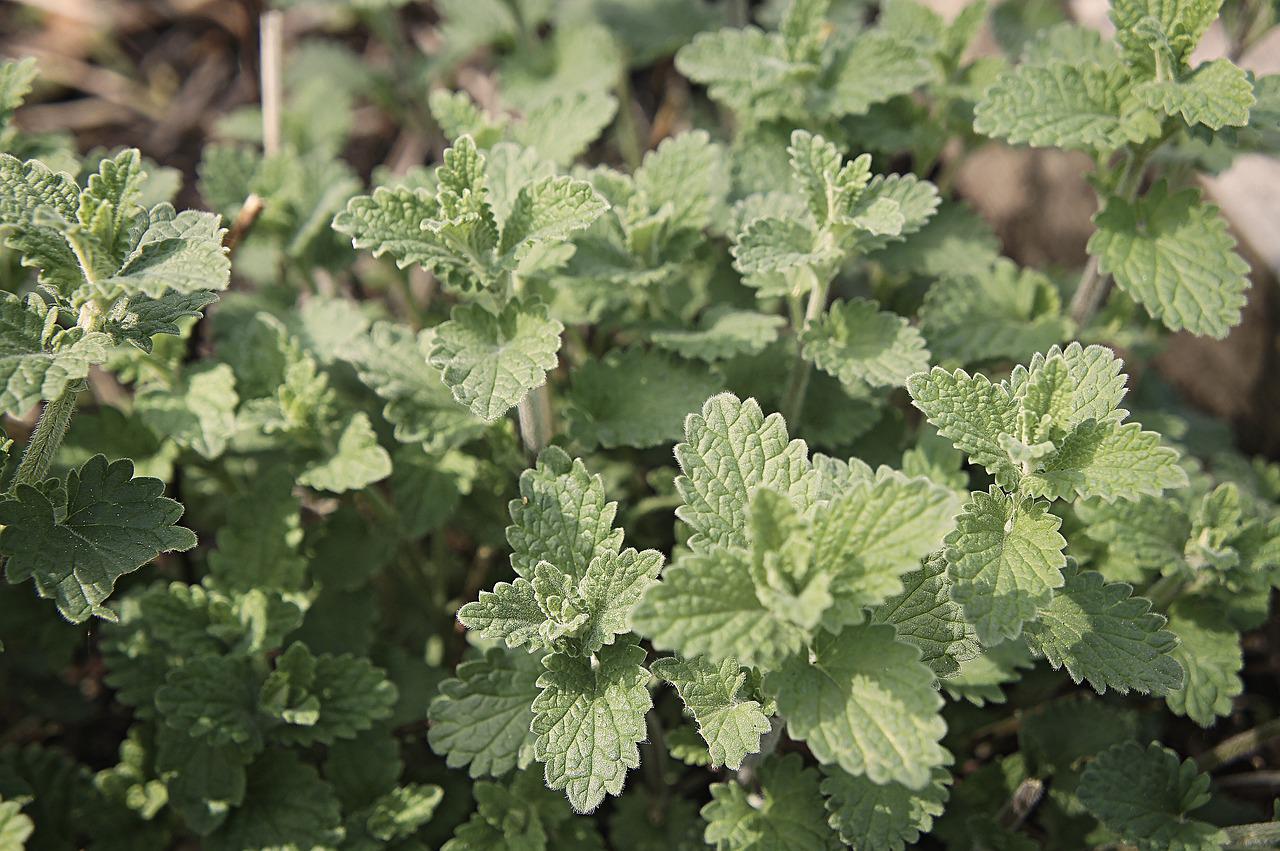
Scullcap (scutellaria lateriflora)
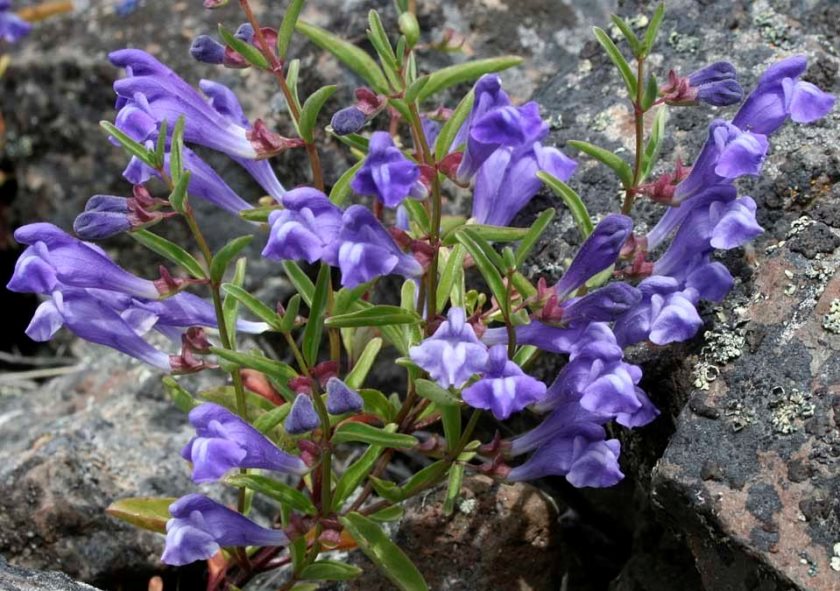

Lateriflora and Baicalensis are the two most common varieties of skullcap from the mint family. Lateriflora derives from native American soil and basicalensis is a traditional Chinese herb. Although related, they treat very different ailments.
Traditionally American scullcap was used as an emmenagogue by Indian elders, to bring on the menstrual cycle of young girls. In the 19th and early 20th centuries, physicians used it as a nervine to treat anxiety caused by physical health issues, mental exhaustion and heart disorders. In the last few centuries, lateriflora has also been used to assist people experiencing mild depression, insomnia and to improve mood. Research appears to support the hypothesis that skullcap stimulates gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), a neurotransmitter that helps calm nervous, thereby positively impacting mood and reducing anxiety. In this way, it works similar to many anti-anxiety medications.
Herbalists often turn to scullcap as a good all-round ‘nerve food’ for its ability to reduce nervous tension and regenerate the central nervous system during periods of stress. For those times in our lives when it’s not logistically possible to reduce some of the sources of stress, skullcap can be the perfect daily tonic.
Propagation is by seed, cuttings or root division. Plant in a sunny, well-draining soil or if you would prefer the plant doesn’t take over your garden then keep in a pot. Harvest the leaves and flowers once it is in full bloom. It will die back in winter and resurge in Spring.
The ideal dose is 1-2 teaspoons of dried herb steeped in boiling water for 10-15 minutes, 3 times a day. It is quite bitter, so you may want to add honey or other herbs like mint to improve the tea flavour. Best to start on a low dose and build up slowly. It also has immediate therapeutic effects that can make you sleepy.
Scullcap is a relaxant and sedative that can trigger side effects such as drowsiness, confusion and irregular heartbeat, so consult your GP before taking this herb. Scullcap is known to interact with some medications. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid it altogether. Large doses and long-term use are associated with liver damage.
Vervain (verbena officinalis)
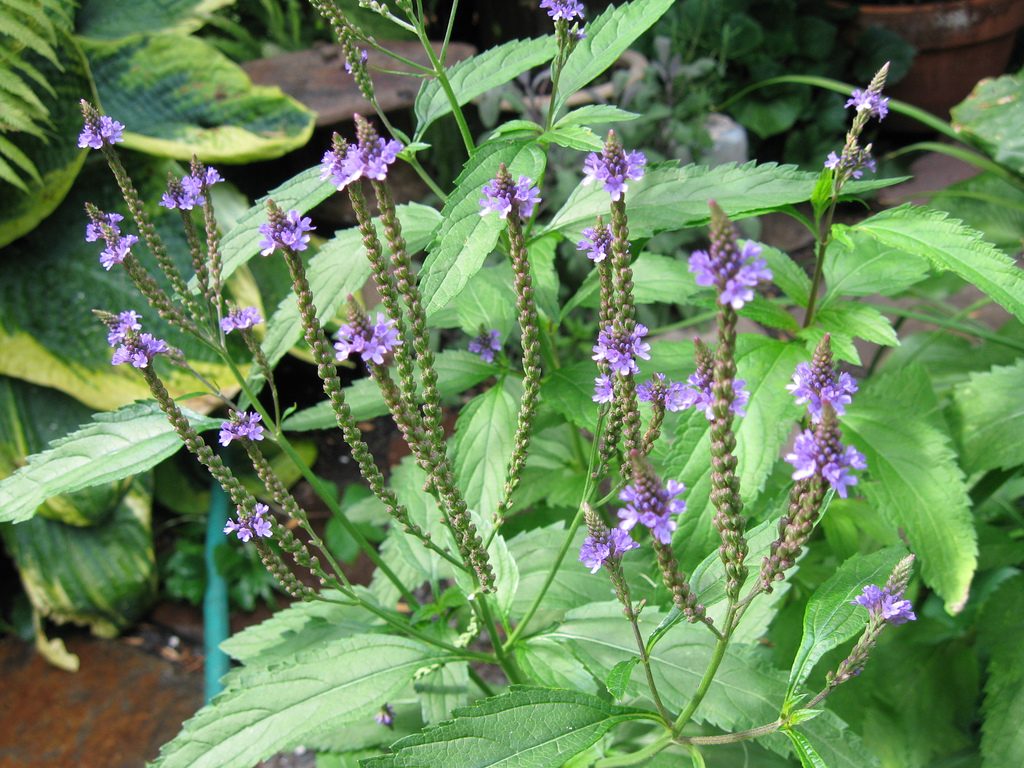

Vervain is such an amazing healing herb that has been used in folk medicine to treat a whole range of different ailments. Legend has it that after the body of Jesus was removed from the cross, vervain growing nearby was pressed onto the wounds. Military physicians during the French revolution used it extensively for pain and wound management. During the Middle Ages, it was used for numerous skin and hair ailments. Since then, the list of applications for physical health has grown exponentially. In more recent times, the focus has also been on mental health benefits.
Like other nervines, vervain has been shown to strengthen the nervous system by reducing stress, tension and anxiety, promoting feelings of calm and relaxation. It has natural tranquilising effects for those suffering from restlessness, irritation and insomnia. Giving our body the opportunity to ‘rest and digest’ during our stressful busy lives is critical, so our nervous system experiences calm and our hormones are balanced. Vervain has also been used extensively with those experiencing depression, low nervous energy and lack of motivation, due to its energy boosting and tonic properties.
Vervain has attractive white to purplish flowers appearing in late Spring and Summer. Propagation is by seed, root division or cutting. Plant in full sun in well-draining soil. It is frost resistant but does not cope with drought.
Make a tea of ½-1 teaspoon of dried or 3 teaspoons of fresh herb in a cup of water, for 10-15 minutes. It is quite bitter, so you may like to add honey or lemon to mask the flavour. Drink up to 3 cups a day.
Vervain used in excess may cause nausea and vomiting. It can interfere with hormone therapy and blood pressure medication. Pregnant women should avoid it, due to its association with uterine contractions.
Gotu kola (centella asiatic)
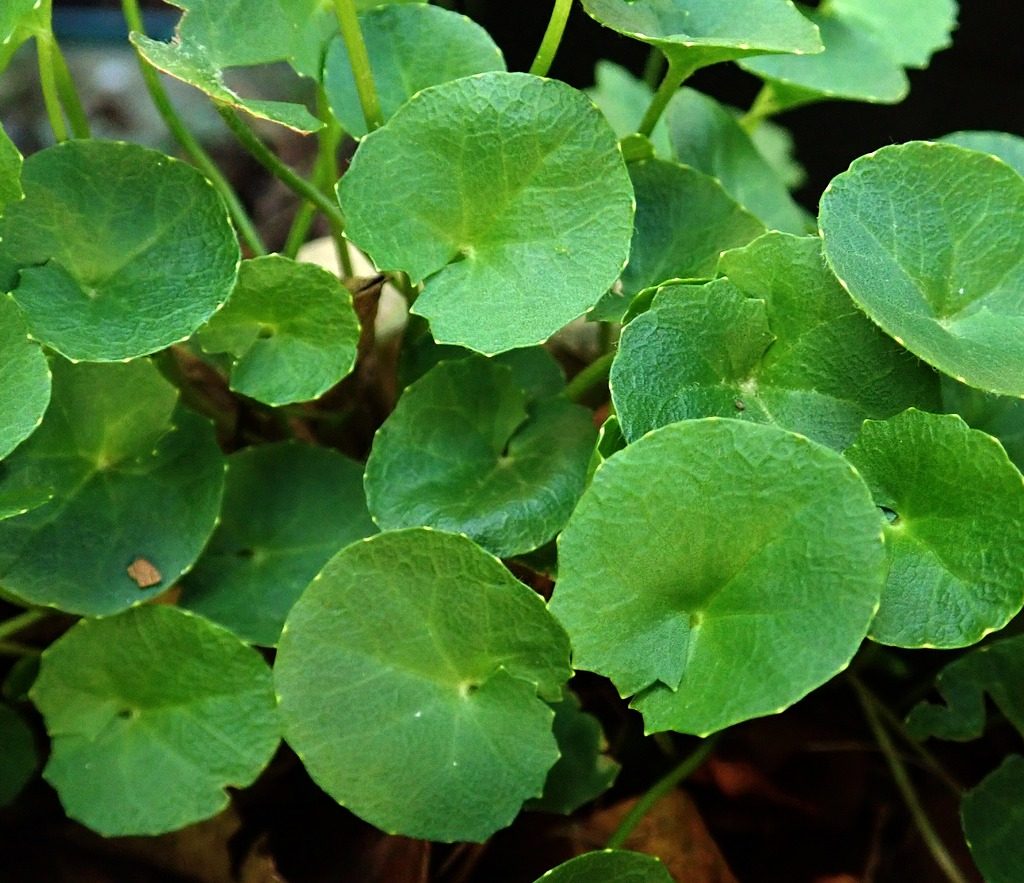

Like lemon balm, gota kola also has a centuries old history of being the ‘elixir of life’, increasing brain capacity and promoting longevity. However, lots of people now say, ‘eating a few leaves a day, keep arthritis away’. In Ancient China it was the key ingredient in their ‘fountain of youth’ elixir. The Chinese herbalist, Professor Li Chung Yun who lived to 256 years old proclaimed amongst various tips for a long stress-free life to include daily consumption of gotu kola and ginseng. In Ayurvedic medicine, gotu kola is valued for boosting nerve and brain cell function, promoting calmness and mental clarity, and improving poor memory and concentration. In the early 1930’s, biochemical studies proved gotu kola was influencing the replacement of biogenic amines, the brain neurotransmitters involved in learning, memory, attention and concentration. More recent research has shown gotu kola can relieve symptoms of attention deficit and hyperactive conditions such as ADHD.
A 2016 study on mice demonstrated gotu kola reduced anxiety induced behaviour, and that same year a small study on humans showed the herb reduced stress, anxiety and depression after 60 days. However, more research is needed.
Gotu kola is a ground cover and can be easily mistaken for pennywort or native violet. Propagation is by root division of the plant or seed. Gotu kola thrives in tropical and subtropical climates. If growing in more temperate regions, put in a large pot or Styrofoam box so you can shift it into a warm position in winter, and out of frosts. Fertilize regularly for the best growth.
Just like Professor Li, it’s best to make taking gotu kola a daily habit. Start with just one or two leaves in the morning and work up to 4-6 leaves a day. You can pick straight from the garden and chew it or chop and add it to food. The herb can also be dried and used as a tea; however, this is one herb where fresh is best. You may be tempted to take more to achieve more effects, however this is not advised. Some serious side effects have been anecdotally reported. Gotu kola is not recommended for children or for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Whilst this article has outlined some of the medicinal herbs that can support your own mental health, make sure you do your own research. This can include spending some time with the plants you are considering. What are you noticing as you sit with them? Does it feel in your gut it is the right thing to try? You should always listen to what your body is telling you. If you are not sure, then find out more information. One of those people you should always consult before taking any herb is your healthcare practitioner, especially if you suffer from an existing medical condition or are on medication, to ensure there are no contraindications and to monitor any potential side effects.
Happy healing herb growing!
References:
‘How Can I use Herbs in my Daily Life?’ by Isabel Shipard
The Botanical Institute
The Lost Herbs
Healthline.com
Restorative Medicine
Webmd.com


















 While some research findings have limitations, here are some of the trends worth noting.
While some research findings have limitations, here are some of the trends worth noting.



 The impact of stress usually results in deteriorating work performance, taking more time off and running down your immune system. Illness has a direct effect on both the quality and quantity of your work. You will work more slowly than usual, make more mistakes or need to repeat tasks. This lower labour productivity translates to increased costs for employers.
The impact of stress usually results in deteriorating work performance, taking more time off and running down your immune system. Illness has a direct effect on both the quality and quantity of your work. You will work more slowly than usual, make more mistakes or need to repeat tasks. This lower labour productivity translates to increased costs for employers.
