Did you know that up to 40% of the nutrients you eat goes into feeding your brain?
The food you eat not only fuels your physical health but new research shows it affects our mental health too!

Is your brain foggy and lethargic, ruminating and making you feel depressed, or overactive and anxious? So what is it you are putting into your body? If we’re really going to make a difference in how we feel and think, then we have to look at what we are feeding our brain.
We need to start taking a different approach to treating mental health, because medication alone is not the answer. If it were, then we wouldn’t be having a global mental health crisis right now. Globally, the number of people taking antidepressants, anti-anxiety and anxti-psychotic medication has doubled over the last five years to 17 percent of the adult population.
So I want to shine the light on nutrition to improve your mental health.
You’re not going to like what you read because this requires a move away from ultra-processed foods which are usually cheap and convenient. The Western diet is typically high in calories, refined grains and sugar, heavily processed, high in chemicals and low in fresh produce. These foods are packed out with ingredients like starch, vegetable oil and sugars along with additives like colours, flavours and emulsifiers so they are cheap to buy but offer no nutritional goodness.
So what is it your brain actually needs so that it can function at its best and having you thinking and feeling great? Fish oil is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids that are key to good brain function. But the real jewels for a mentally healthy diet I want to introduce you to are micronutrients. Unlike their much bigger cousins’ macronutrients – carbs, proteins and fats – micronutrients are vitamins and minerals.
Minerals are the stable chemical compounds like calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and potassium and the trace minerals like zinc, copper, iodine and selenium. Vitamins are organic compounds which are generally not made in the body, we have to consume them through plants. There are about 15 essential vitamins with a variety of letters and numbers which you are probably familiar with.
Most of us are not getting all the necessary micronutrients from real foods that is needed for a mentally healthy brain! In a recent US study, 94 % of the US population did not even meet the daily requirement for Vitamin D, 89% for Vitamin E, 52% for magnesium, 44% for calcium, 43% for Vitamin A and 39% for Vitamin C. Could this be the reason why so many of us are struggling with depression and anxiety?
So what is it about these micronutrient little gems that is so key to our mental health? Well, this is where it gets a little complex because it is about understanding a bit of brain chemistry.
Micronutrients are key to our brain being able to make neurotransmitters such as serotonin, you probably know as the ‘happy hormone’. It’s the chemical that contributes to our feelings of wellbeing, stabilizes our mood and plays a role in regulating our sleep, learning, memory and appetite. Without it, we feel depressed.
Micronutrients are also vital in assisting the mitochondria, or energy organelles of your cells to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle, produces ATP and is completely dependent on micronutrients to function.
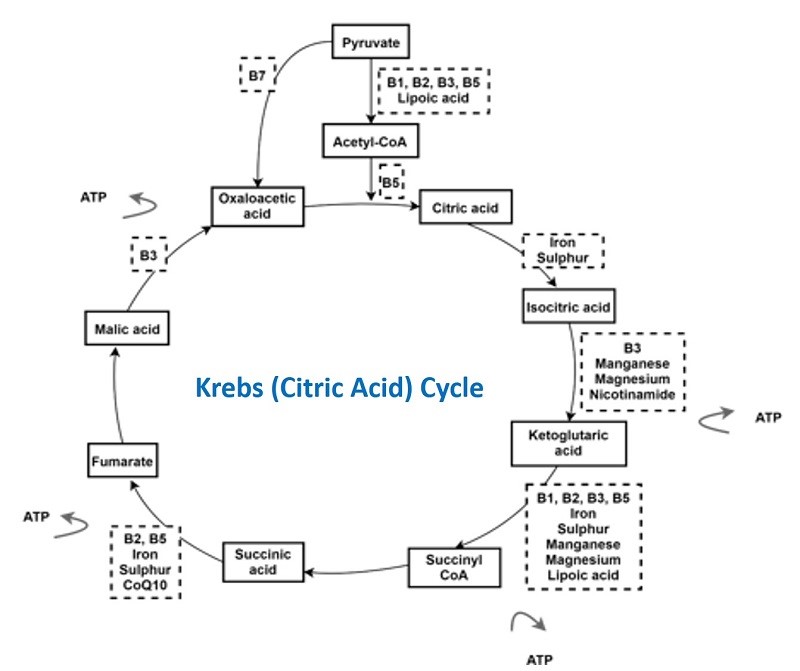
Take a close look at how many micronutrients are involved in this cycle? Mind blowing.
But wait there’s more.
“In every organ of our body, including our brain, compounds or chemicals go through multiple conversions. So from chemical A to chemical B. It’s that simple. And to make that conversion work, you need enzymes and cofactors. Consider enzymes as the tools needed to assemble a car. The enzymes are the tools used to build the car, but they are dependent upon having plenty of factory workers. Without the workers, the assembly just won’t happen, but with more of them, assembly will go faster. Minerals and vitamins are your factory workers. So in other words, you need to feed your brain a steady supply of micronutrients to provide the co-factors needed for brain metabolism to happen.” (Rucklidge)
So let’s use our happy hormone as an example. We need to consume the chemical tryptophan in order for it to convert into the neurotransmitter, serotonin. And in order to make the conversation, we also need iron, phosphorus, calcium and vitamin B6. For serotonin to breakdown we need niacin and riboflavin, as well as molybdenum. Other steps required for the breakdown of tryptophan, requires calcium, potassium, iron, zinc, copper, thiamine, riboflavin and niacin. So all up there are 11 micronutrients required for three steps in the chemical pathway of converting tryptophan to serotonin. Complex isn’t it? Makes you wonder what happens when one or more of these crucial ingredients is missing from our diet? Is it no wonder so many of us are depressed when our diets are so poor?
These same types of complex metabolism processes are required to make all neurotransmitters. Dopamine, the pleasure hormone, which requires the amino acid tyrosine may have a role to play in the diagnosis of schizophrenia, ADHD and Parkinsons Disease. GABA, the relaxing chemical, is responsible for slowing down the brain and central nervous system, creating a sense of calm, lowering anxiety and reducing mental and physical stress. So the key message here is, we need a broad range of micronutrients in order to optimize brain metabolism and function, to operate at our physical and mental best.
So now you know why and how micronutrients are like gold for our mental health, you probably just want to know what specific foods you should be eating. Well, here is one list. It is considered to be the most micronutrient-rich anti-depressant foods, according to psychiatrists Laura LaChance and Drew Ramsey beginning with the most beneficial.

Animals Foods
Oyster
Liver and organ meats
Poultry giblets
Clam and muscles
Octopus
Crab
Goat
Tuna
Lobster
Rainbow Trout
Salmon
Herring
Emu
Snapper

Plant Foods
Watercress
Spinach
Mustard, turnip or beet greens
Lettuces
Swiss chard
Fresh herbs
Chicory greens
Pummelo
Peppers
Kale or collards
Pumpkin
Dandelion greens
Cauliflower
Kohlrabi
Red cabbage
Broccoli
Brussel sprouts
Paw Paw
Lemon
Strawberry
Other research has shown increasing foods high in tryptophan like milk, turkey, chicken and oats reduces depression risk, and maintains appropriate melatonin levels, which aids a good night’s sleep.
Research shows that the Mediterranean diet stacks up well against the criteria for better brain health, rich in vitamins, minerals and essential fatty acids. How would your diet stack up? Are there some small changes you could make to improve your mental health, decrease the impact of stress on your body or reduce depression and anxiety?
I look forward to sharing more resources with you as we explore the role of nutrition in mental health. If a holistic approach to mental health appeals to you, then you may like to check out my services.
References:
Antidepressant foods: An Evidence-Based nutrient profiling system for depression, Laura LaChance & Drew Ramsey, 2018
The role of Vitamins and Minerals in Energy Metabolism and Well-Being, S. Huskisson, S. Maggini & M. Ruf, 2007
The Better Brain: The New Science of Treating, Anxiety, Depression, ADHD and Other Mental Health Disorders With Nutrition, Bonnie J Kaplan & Julia J Rucklidge, 2021
Mental Health and Nutrition, edx course, University of Canterbury, J. Rucklidge